What is Lean Construction? How To Use Lean Tools In Construction Industry?
Lean is a Buzzword of the present construction industry. Lean construction is a systematic methodology with the goal of creating value for customers and reducing the cost of any process by removing waste. Lean tools and techniques are the emerging skills to become productive Engineers. By applying lean tools we can complete the projects in time, reduce cost overrun & time over Run.
Lean construction is a new way to manage the construction of customers’ needs with perfection. The main thing in applying lean in any sector or any industry is to reduce waste and cost overruns throughout the life cycle of the project. LC enables to achieve continuous improvements, construction challenges overcome and lessons learned in one project can be used for future projects. By using this lean management one can reduce time to build and optimize the resources utilization which definitely decreases the time and cost overruns. We know that Small stones can form as a big mountain, in the same way, taking small steps in construction can give us more benefits over time. It mainly focused on the value stream, which means as per customer perception of service, which he will pay for. While doing any work or project, we can come across many activities where we convert inputs into outputs. In this process, activities are classified into 3 types.
Non-value-added activity: these activities do not add any value to the activity, so these activities are wasted, which leads to customer dissatisfaction and he will not pay any costs to these activities. Example: Idle waiting, shifting of bricks from one place to other, etc.
Value-added activity: these activities are main or important to the process of completion, essential for the process which can improve quality and productivity. Example: brickwork, plastering, etc.
Non-value-added but required: these are necessary for continuity of process but customers won’t pay any cost for these activities. Example: supporting work, trench excavation for draining water, etc. All the Non-value-added activity comes under the wastages. Lean focuses on the reduction of wastages that offer no value to customers, delay the progress, weaken the motivation among the people working on site. Less than 30% of the tasks in a process add value from the customer’s perspective. According to a construction industry institute (CII) study, almost 57% of construction activities are coming under wastage. These wastes can cumulatively increase the project cost, so by applying Lean main goal is to turn the wastage into a customer benefit. It is a continuous process of improving which includes communications too. By eliminating these wastes applying Lean management can make the progress of projects more efficient and boost employee productivity so that profits will improve.
Before applying LEAN one have to understand the fundamentals of why we are using the LEAN?
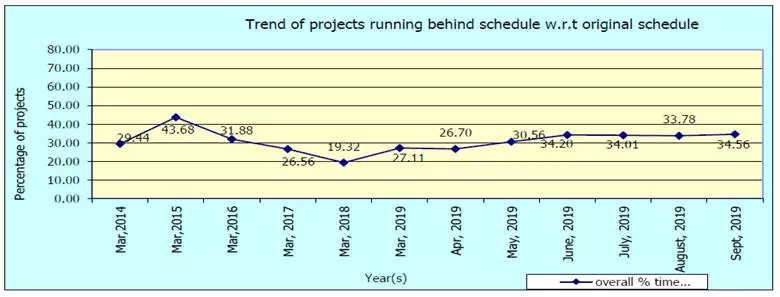
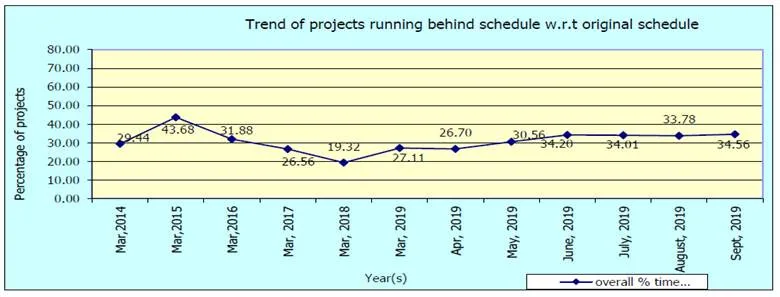
Time over-run:
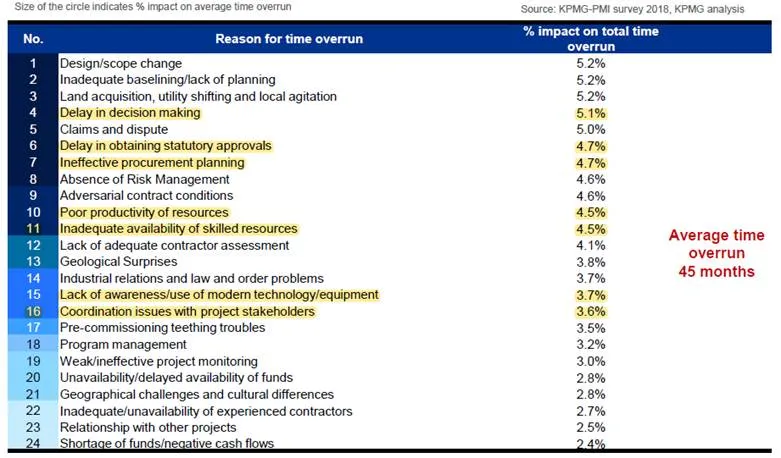
Cost over-run:
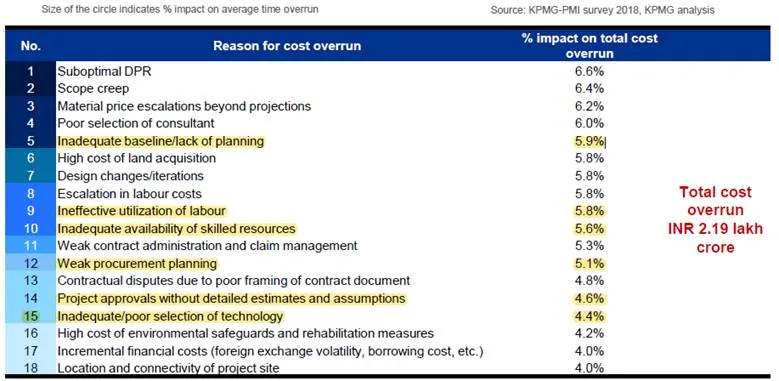
After critically analyzing the above figures shown, every project has to identify the root cause for the failures and wastages incurred in the project. By performing root cause analysis, cumulative root causes for failure of projects are
- Preparatory failure,
- Planning failure,
- Informatory failure,
- Mobilization failure,
- Coordination failures,
- Execution failures,
- Supervisory failure and some other failures which are not noticeable.
So after completion of the project or attending any conference, there will be a blame game among these departments. So Lean planning software (LPS) manages to identify who is responsible for the delay in the progress at the moment itself and after completion also. Lean planning through Lean planning software can emphasize the following:
- Collective Planning
- Getting down to details
- Constraint identification
- The commitment was driven by planning with real-time collaboration
- Continuous improvement
- No blame-game culture
Concept of wastages in LEAN construction:
Recent studies in the USA, Scandinavia, and this country suggest that up to 30% of construction is reworked, labor is used at only 40-60% of potential efficiency, accidents can account for 3-6% of total project costs, and at least 10% of materials are wasted, but in the construction industry, for many people who work on-site or practitioners think that waste is related to the number of materials wasted only. They won’t think about other types of wastes such as Overstaffing, Interference with other crews, insufficient work to perform, Equipment breakdowns, Design Errors, Rework, and Material Shortages. According to taxonomy, wastes of construction divides as follows:
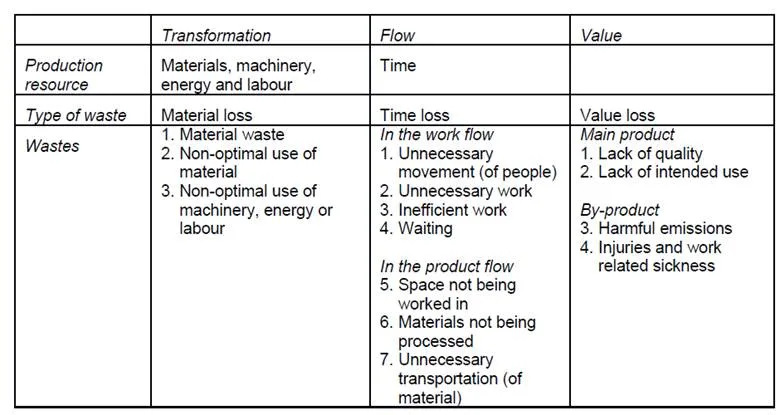
According to lean philosophy, wastes are categorized into 8 wastes. The eight wastes of construction are based on the seven wastes of manufacturing, sometimes known as ‘Muda’ – the concept of lean process thinking, developed by Taiichi Ohno, the Chief Engineer of Toyota. Although they are aimed at the manufacturing industry, it has been found that they also fit the construction industry.
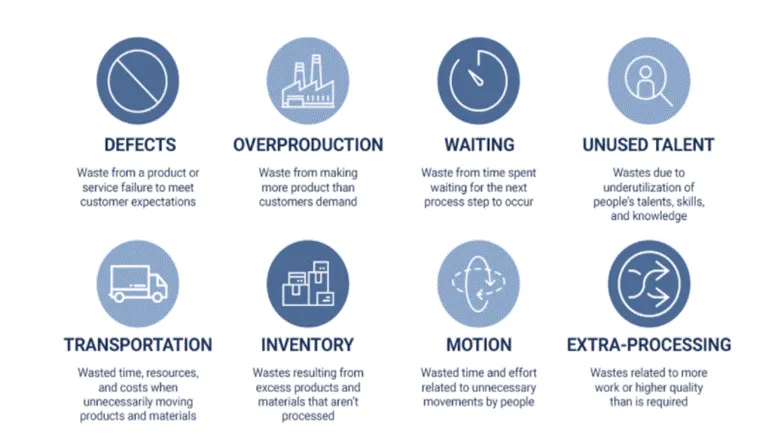
Some Lean tools to eliminate these wastes in construction:
1.PDCA: “Plan, Do, Check, Act”
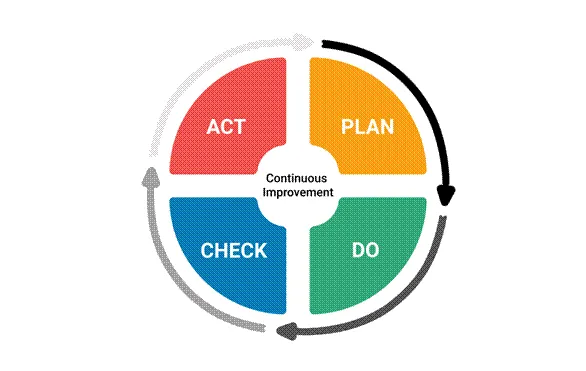
Plan Phase: Selection of material
Do Phase: Test installation is observed carefully and videotaped
Check Phase: Finished work is observed carefully by the PM and his team
Act Phase: Various recommendations were made, was tested and a reduction in the activity cost (up to 38%) was observed
2. Value stream mapping (VSM)
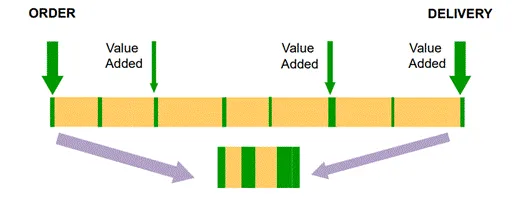
With the help of VSM, you can identify wasteful activities which are nonvalue added. VSM provides a clear view of the work process – where value-adding and non-value-adding stages form. It can show current workflow, future workflow, implementing workflow.
3. Japanese model to improve operations
- Seiri (Straighten up): get rid of discard of unwanted items.
- Seiton (put things in order): orderly arrangement or placing the correct items at the correct place, so that one cannot waste time finding them
- Seiso (Clean up) – cleaning and daily inspection, cleaning the equipment after using and inspecting it before placing it in its place.
- Seiketsu (Personal neatness) – standardization – color coding and labeling
- Shitsuke (Discipline) – Motivate and sustain other 4 Ss – conducting recognition programs.

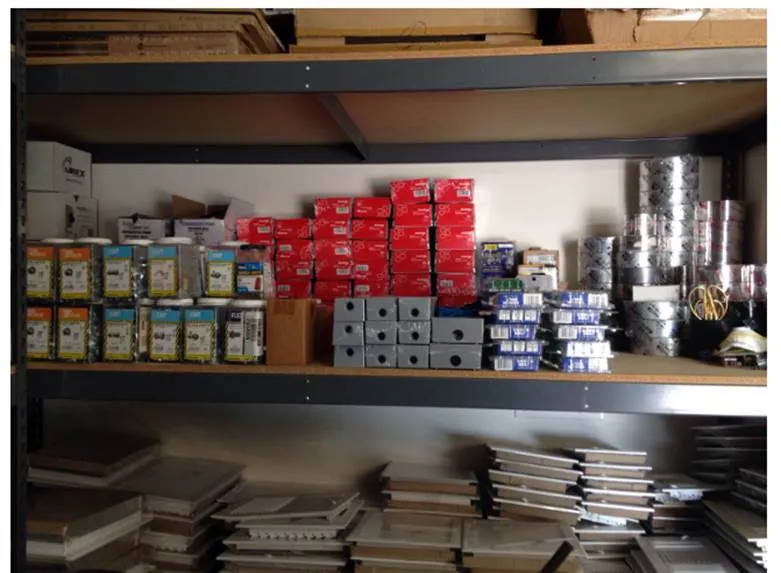
4.Kanban: (visible boards)
Kan-ban is the Japanese word for “Visual Board”. Picture representation so that anyone can identify material that they want easily.
Kanban is used to implement the just in time (JIT) implementation. See the picture below, anyone can identify the items that they want easily in seconds saves our time.

Some other Lean tools and techniques used in the construction industry:
- Last planner system (Lean plan do software for planning the project )
- Building Information Modeling (BIM)
- Big room meeting
- Design system matrix
- Poke-yoke
- Work sampling
- Load leveling
- Quick change over
- Root cause analysis
- Integrated project delivery
- Target value design
To summarize the Lean construction, LC is a way of thinking not a onetime thing, it is a transformational process of cultural change, not a copy-paste solution from one project to another, a process involving everyone not only the planning department or top management, but it is also Pull based process not push-based process. It is not conventional thinking; it is continuous improvement and innovation-oriented.


