Risk Management: Why it’s Important
There is no project in this world without risk. The risk can either be a positive risk or negative. This article explains the introduction of Risk Management and SWOT Analysis.
What is Risk?
An uncertain event that, if it occurs, has a positive or negative effect on the company or project goals and objectives and/ or success.
What is Risk Management?
- A proactive attempt to recognize and manage internal events and external threats that affect the likelihood of a project’s success
- Project Success = Safe – On Time – Under Budget – Quality
- The art and science of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risk throughout the life of a company/project and in the best interest of meeting company/project goals and objectives.
- It begins with fully understanding the organization’s strengths and weaknesses, and the opportunities and threats that it faces.
- It helps in planning for the ‘future’ by exploiting strengths and opportunities and mitigating weaknesses and threats.
What is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
- SWOT Analysis is a planning tool used to analyze risks on a project.
- A Framework for organizing and using historical data and information to identify internal and external risks.
- A technique that enables a project team to move from traditional strategies to a project-specific fresh perspective.
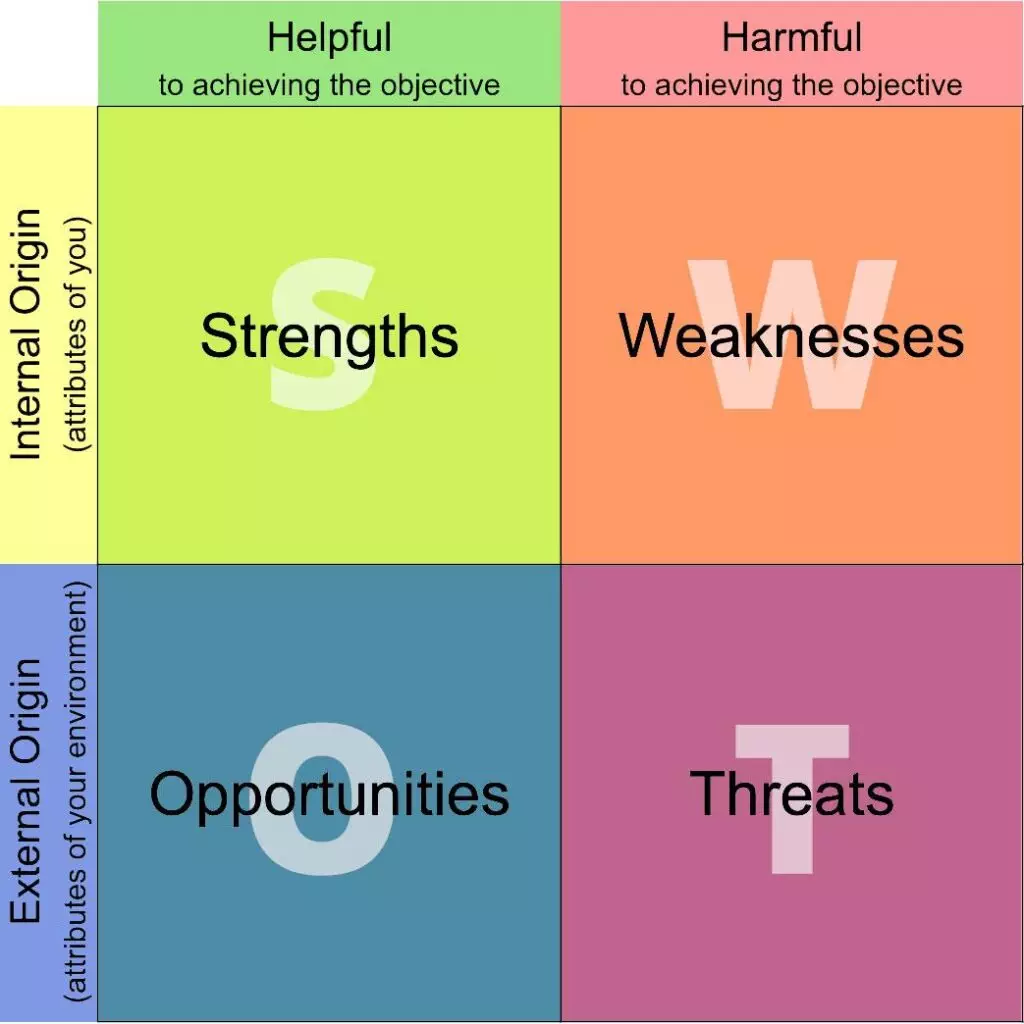
1)STRENGTHS:
- Characteristics of the business or a project team that gives it a competitive advantage.
- Positive tangible and intangible attributes, internal to an organization.
- Beneficial aspects of the organization or the capabilities of an organization, which include human competencies, process capabilities, financial resources, products and services, customer goodwill, and brand loyalty.
- Identify skills and capabilities that you have.
- What can you do particularly well, relative to competitors?
- What do analysts consider to be your strengths?
- What resources do you have?
- Is your brand or reputation strong?
2)WEAKNESSES:
- Characteristics that place the firm at a disadvantage relative to competitors.
- Detract the organization from its ability to attain the core goal and influence its growth.
- Weaknesses are the factors that do not meet the standards we feel they should meet. However, weaknesses must be controlled, minimized, and eliminated.
- What do competitors do better than you?
- What do you do poorly or least effectively?
- What generates the most customer dissatisfaction and
- complaints?
- What generates the most employee dissatisfaction and
- complaints?
- What processes and activities can you improve?
3)OPPORTUNITIES:
- Chances to increase revenue – External factors that represent the reason for an organization to continue to exist & develop.
- Arise when an organization can take advantage of conditions in its environment to plan and execute strategies that enable it to become more profitable.
- The organization should be careful and recognize the opportunities and grasp them whenever they arise. Opportunities may arise from the market, competition, industry/government, and technology.
- Where can you apply your strengths?
- How are your customers and their needs changing?
- How is technology changing your business?
- Are there new markets for your strengths? (e.g., foreign)
- Are your rivals’ customers dissatisfied?
4)THREATS:
- External elements in the environment that could cause trouble for the business – External factors, beyond an organization’s control, which could place the organization’s mission or operations at risk.
- Arise when conditions in the external environment jeopardize the reliability and profitability of the organization’s business.
- Compound the vulnerability when they relate to the weaknesses. Threats are uncontrollable. When a threat comes, stability and survival can be at stake.
- Are customers able to meet their needs with your competitors?
- Are customers’ needs changing away from your market?
- What new technologies are your competitors developing?
- Are your rivals improving their market offerings or lowering prices?
- Is new technology making your operations obsolete?
- Is your cash-flow and debt position healthy?
- Are your employees satisfied? Is turnover high?
- Is new competition coming?
- Are sales growing slower than the industry average?
Why SWOT Analysis?
- To help decision-makers share and compare ideas.
- To bring a clearer common purpose and understanding of factors for success.
- To organize the important factors linked to success and failure in the business world.
- To analyze issues that have led to failure in the past.




